- Shanghai Zhongshen International Trade Co., Ltd. - Two decades of trade agency expertise.
- Service Hotline: 139 1787 2118
On March 31, 2023, Japans Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry announced new semiconductor export control regulations - Draft Order Partially Amending the Order Specifying Goods or Technologies Under the Export Trade Control Order Appendix 1 and Foreign Exchange Order Appendix - proposing to expand the scope of advanced chip manufacturing equipment requiring ministerial pre-approval before export, with public comments accepted until April 29, 2023.
Under the new regulation, Japan will expand the scope of controlled chip manufacturing equipment, adding 23 categories of semiconductor manufacturing equipment and related technologies. This means Japanese exporters will need prior approval from the Minister of Economy, Trade and Industry to export these items. Additionally, for exports to other countries and regions, including China, theEquipment Exportlicense application process will become more stringent and complex,as follows:
Addition of 23 categories of semiconductor manufacturing equipment and corresponding technologies, expanding Japans controlled list. Most of these are for processes below 14nm to 10nm. The new categories include cleaning equipment (3 items), thin-film deposition equipment (11 items), heat treatment equipment (1 item), lithography equipment (4 items), etching equipment (3 items), and testing equipment (1 item).
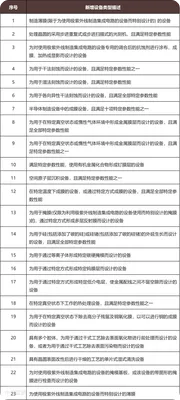
2. Exports to China will face stricter, more complex licensing mechanisms including applications for Specific General Export Licenses.
3. For technologies related to newly added items: if concerning use of such items, licensing requirements for mainland China, Hong Kong or Macau will be significantly stricter and more complex than those for 42 specified countries/regions; if concerning design/manufacture, all countries will uniformly require Specific General Export Licenses.
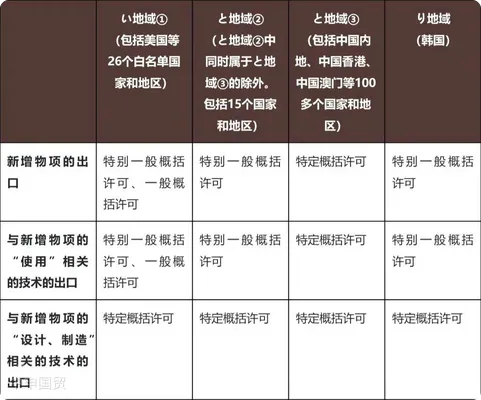
The impacts of the new regulation and key follow-up points are as follows:
Impact on Japanese semiconductor equipment exporters: The new regulation expands Japans controlled list, requiring stricter license applications for exports of the 23 categories of equipment and technologies, potentially affecting their export business and profits.
Impact on Chinese semiconductor companies: The stricter license application mechanism means higher export costs and longer wait times for Chinese semiconductor companies, potentially affecting their production and R&D plans.
Impact on the global semiconductor supply chain: As a key player in the global semiconductor supply chain, Japans new regulation may affect supply chain stability. Affected companies will need to reassess their supply chain strategies and consider alternative sources.
In the coming months, the following key points require attention:
Japanese government decisions: Close monitoring of the governments stance and actions in implementing the new regulation. How it interprets, enforces, and resolves issues will significantly impact the semiconductor industry.
China-U.S. relations: As Japan tightens controls on Chinese semiconductor companies, China-U.S. relations may further deteriorate, potentially triggering trade disputes and political conflicts affecting the global semiconductor industry.
Global semiconductor supply chain: Close monitoring of developments in the global supply chain, including adjustments among semiconductor manufacturers partners and suppliers and changes in production capacity, to timely adjust business strategies.
Related Recommendations
? 2025. All Rights Reserved. Shanghai ICP No. 2023007705-2  PSB Record: Shanghai No.31011502009912
PSB Record: Shanghai No.31011502009912










