- Shanghai Zhongshen International Trade Co., Ltd. - Two decades of trade agency expertise.
- Service Hotline: 139 1787 2118
Against the backdrop of the increasingly fierce competition in the global semiconductor industry, the US Department of Commerce has recently updated the export control provisions, which is another major adjustment after the Chip Act. This update targets the core technologies and equipment for chip manufacturing, including but not limited to EUV masks, etching machines, etc., and at the same time re - clarifies the AI chip license and its exceptions. This move aims to restrict the development of the semiconductor industry in mainland China, especially to block its leap to advanced process technologies.
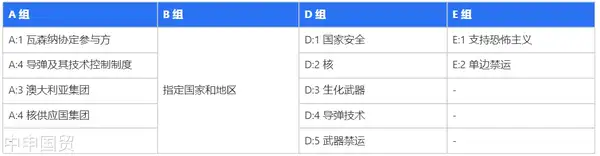
I. Special Mention of Macau Region and D:5 Group of Regions
This export control update frequently mentions Macau, aligning with October 2023 rules by applying presumption of denial to Macau and D:5 regions (including mainland China, Iran, Russia). This means controlled AI chip export applications to these regions will be denied by default absent exceptional circumstances. D:5 is a US export control category imposing strict restrictions.
II. Authorized Advanced Computing License Exemption
The update introduces Authorized Advanced Computing license exemptions, facilitating certain exports. Specifically, AI-related product exports to non-D:4/D:5 regions dont require additional licenses if conditions are met.
III. Impact on Lithography Machines, RTX4090 and AIPC
(1) Lithography Machines:This update strengthens EUV mask and equipment controls, adding national security and regional stability as new control reasons, imposing stricter licensing requirements for Macau and D:5 regions.
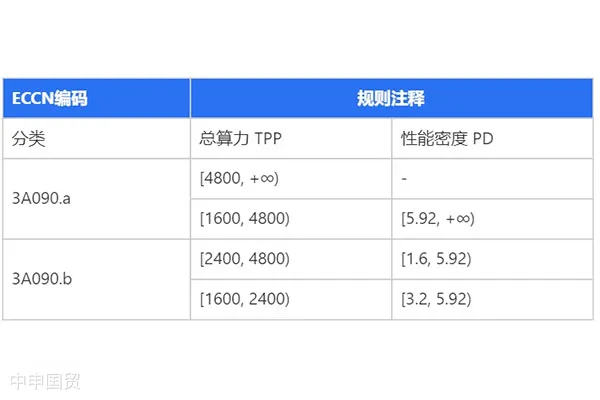
(2) RTX4090:For consumer-grade AI chips like the RTX4090, the updated clauses clarify the calculation method and thresholds for performance density, providing clear guidance for the export of certain high-performance chips.
(3) AIPC:For AI processing chips (AIPC), the updated terms provide a clearer scope of application and exceptions, giving enterprises a more definite basis when exporting such products.
IV. Control Objectives and Countermeasures
The main purpose of this update of US export controls is to restrict China from acquiring advanced technologies and equipment in the semiconductor industry, especially those key technologies that can be used in military and advanced computing. In this way, the US hopes to maintain its technological leadership in the global semiconductor industry. At the same time, for national security considerations, it aims to prevent advanced technologies from falling into the hands of potential opponents.
Faced with this situation, Chinese enterprises and research institutions need to adopt a number of countermeasures:
(1) Strengthen independent research and development:Improve the ability of independent research and development and reduce dependence on external advanced technologies and equipment.
(2) Diversify import sources:Explore technological cooperation and equipment procurement from other countries and regions to reduce dependence on a single source.
(3) Comply with laws and regulations:Strictly abide by US export control regulations and introduce technologies and equipment through legal channels.
(4) International cooperation:Strengthen communication with international partners, jointly respond to the US technology blockade, and seek alternative technological paths.
The update of US export controls reflects its strategic considerations in the global semiconductor industry competition. Although the degree of control has been adjusted, its fundamental purpose remains unchanged. Chinese enterprises need to pay close attention to subsequent developments, flexibly adjust their strategies, and strengthen independent technology research and development to cope with the changing international trade environment.
Related Recommendations
? 2025. All Rights Reserved. Shanghai ICP No. 2023007705-2  PSB Record: Shanghai No.31011502009912
PSB Record: Shanghai No.31011502009912










